All types of investors use hedging as a strategy to protect a position from adverse price movements. Typically, hedging involves opening a second position that may be negatively correlated to the main asset held, meaning that if there is an adverse move in the price of the main asset, the second position will undergo a complementary and opposite move to offset those losses.
In Forex trading, investors can use a second currency pair as a hedge against existing positions that they are unwilling to close. While hedging reduces risk at the expense of profit, it can be a valuable tool for protecting profits and avoiding losses in forex trading.
The basics of forex hedging
Forex hedging involves opening a position in one currency pair to offset possible movements in another currency pair. Assuming that these positions are the same size and that price movements are inversely correlated, the price changes in these positions can cancel each other out while they are both active.
While this eliminates potential profits during this window, it also limits the risk of losses.
The simplest form is a direct lock-in hedge, where traders take a buy position and a sell position on the same currency pair in order to preserve any profits they have already made or prevent any further losses. Traders can take a more sophisticated approach to hedging, taking advantage of the known correlation between two currency pairs.
How does Forex hedging work
The process of opening a forex hedge is simple. It starts with an existing open position - usually a long position - and your initial trade is expected to move in a certain direction. Hedging is done by taking a position that moves in the opposite direction of the currency pair you expect, so that you can keep your open position on the original trade without incurring a loss if the price moves in the opposite direction to your expectations.
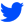
Typically, this hedge is used to preserve the gains you've already made. The NOK/JPY below shows a situation where a trader might want to hedge. For example, if they open a long position near the low of the chart and take advantage of the large gains that form in the days that follow, the trader may choose to open a short position to hedge against any potential losses.
While traders can also simply close their positions and cash out their gains, they may be interested in keeping that open position and seeing how chart patterns and technical indicators change over time.
In this case, hedging can be used to offset potential profits or losses as the trader maintains the position and gathers more information. Even if prices plummet, they were able to cash in all the gains they generated from the initial rise.
Advantages of Forex hedging
Similar to hedging in the stock market, Forex hedging offers several key benefits where experienced traders can stabilize their accounts and holdings. These advantages include:
You have more control over risk/rate of return. Hedging provides a valuable balance against your other positions and can provide a price increase in the form of ballast, even if the other positions move in the opposite direction.
It increases the diversification of your positions. Hedging spreads your open positions to reduce the risk of a single variable or event causing a total loss to your position.
It acts as an insurance policy against unpredictable price fluctuations. If volatility or sudden price movements occur, your hedging position can help preserve the overall value of your account and create a profit on that position, which can stabilize your account balance until other positions increase in value.
Potential drawbacks of Forex hedging
While hedging can be a very valuable strategy, it also comes with significant risks that can wipe out gains and profits if you don't use these sets of hedges carefully. The most likely disadvantages of hedging include the following:
Your profit potential may be reduced. While hedging reduces your risk, it also cuts into your profit potential. This is because if the profit on your initial open position continues to rise, your hedge position may decrease.
You may lack the expertise to leverage hedging for your own financial gain. Due to the complexity of creating and timing hedges, many starting forex traders lack the market familiarity and expertise to execute hedges in a way that maximizes their value.
In the event of sudden volatility, you may also lose money on your hedge. While this may not be a common event, hedges - especially complex hedges that are not directly linked to your other positions - do not always guarantee a gain in value when other positions are lost. This is because the variables and events that cause these price movements cannot be fully predicted, which means that the impact of volatility on your hedging position cannot be fully understood. This can lead to bigger losses than if you had not hedged your position at all.
Complex hedging in forex
Because complex hedges are not direct hedges, more trading experience is required to execute effectively. One way to do this is to open a position in two currency pairs where price movements tend to be correlated.
Traders can use correlation matrices to identify forex pairs that have a strong negative correlation, meaning that when one currency pair rises in price, the other currency pair falls.
For example, a combination of USD/CHF and EUR/USD is an excellent choice for hedging because they have a strong negative correlation. By establishing a buy position on USD/CHF and a short position on EUR/USD, traders can hedge their positions on USD to minimize their trading risk.
Trading with forex options also creates hedging opportunities, which can be very effective in certain situations. This requires experienced traders to be able to identify these small Windows of opportunity, and sophisticated hedging can help maximize profits while minimizing risk.
When to consider hedging
Hedging is useful whenever you want to maintain a paired open position while offsetting some of your risk in this situation.
Short-term hedging can be a good way to protect profits when you are unsure of certain factors that may be causing price fluctuations. This uncertainty can range from a suspicion that an asset is overbought to a fear that political or economic instability could cause the value of certain forex pairs to plummet - especially if you have taken a long position in those pairs.
In the USD/JPY chart shown below, a period of consolidation is creating breakout potential that could go in any direction. If you already have an open position in this currency pair and want the price to fall above the resistance line, you can consider hedging with another position with the goal of recovering from the trend line to the previous high.
If you do open this hedge and the price breaks the trend line, you can always close your second position and continue to reap the profits of your successful short position. But if you're wrong and the trend reverses, you can close both positions and still cash in your gains from the previous price change.
Traders often use hedging to protect against short-term fluctuations in economic news releases or weekend market gaps. Traders should keep in mind that hedging reduces trading risk as well as potential profits.
Due to the low returns from hedging, this strategy is best suited for traders who work in the forex market full time, or who have accounts large enough to generate large monetary gains with a limited percentage of profits.
Exit hedge
When you exit a direct or complex hedge and keep your initial position, you only need to close the second position. However, when you close both sides of the hedge, you need to close those positions at the same time to avoid potential losses that could occur if a gap occurs.
It is important to keep track of your hedging positions so that you can close the right positions at the right time to complete the execution of this strategy. Ignoring an open position in the process can derail your entire hedging strategy - and potentially expose your trading account to huge losses.
Potential risk when hedging
While forex hedging is often used to limit a trader's risk, poor execution of this strategy can be disastrous for your trading account.
Due to the complexity of forex hedging, traders - even experienced ones - can never be fully guaranteed that their hedges will offset any possible losses. Even with a well-designed hedge, both sides are likely to incur losses. Factors such as commissions and swaps should also be carefully considered.
Traders should not engage in complex hedging strategies until they have a strong understanding of market volatility and how to time trades to take advantage of price fluctuations. Poor timing and complex pairing decisions can lead to rapid losses in a short period of time.
Experienced traders can use their knowledge of market fluctuations, the factors that influence these price movements, and strong familiarity with forex correlation matrices to protect their profits and continue generating income by using timely forex hedges.

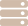
 Source:Valutrades
Source:Valutrades